Spiral fin tubes are high - performance heat - exchange components engineered to boost thermal efficiency across diverse
industrial and commercial scenarios. Their unique spiral - fin structure maximizes the heat - transfer surface area, enabling
rapid and effective heat exchange between media. Ideal for applications like heat exchangers, HVAC systems, and industrial cooling
units, these tubes deliver reliable performance in both high - and low - temperature environments.
Products Description


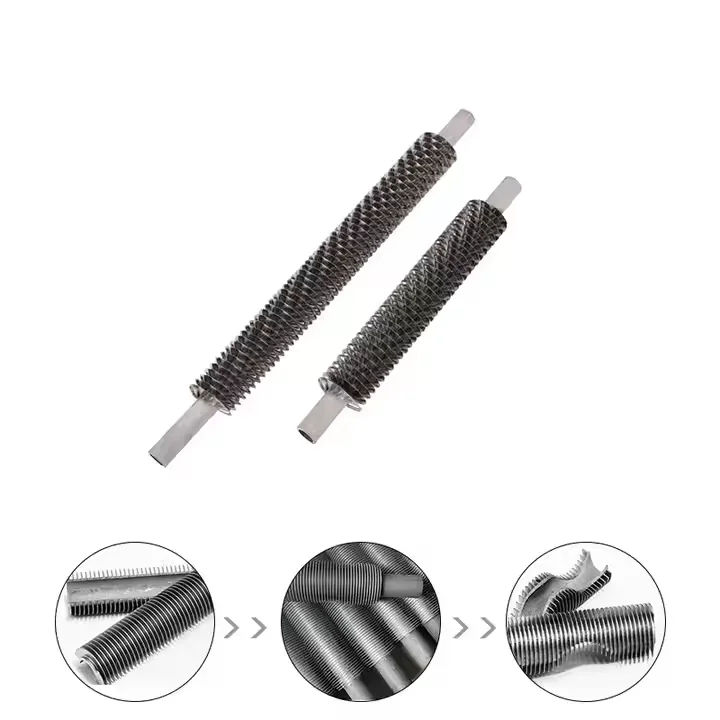
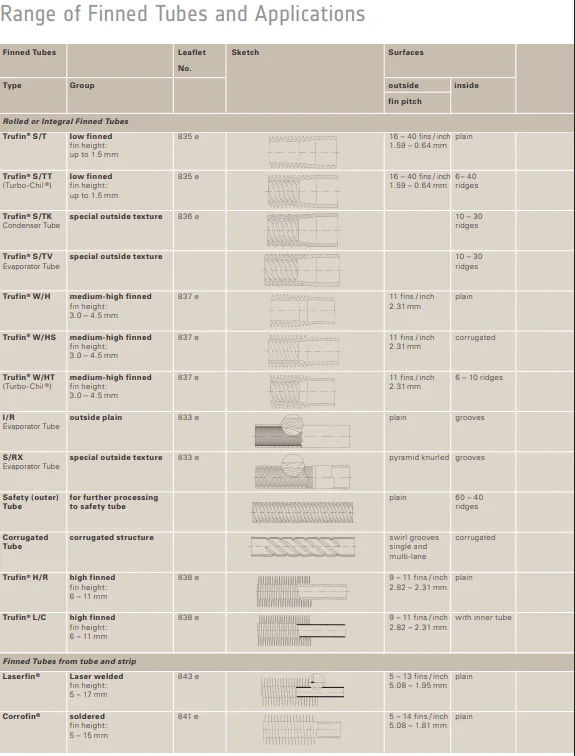
Spiral finned tube



Structural & Dimensional Parameters
Tube Diameter
We offer a flexible range of base tube diameters, from 12mm (small - scale precision applications) to 100mm+ (large - flow
industrial systems). Common sizes like 19mm, 25mm, and 38mm suit most standard heat - exchange setups, while custom diameters
address specialized flow and pressure needs.
Fin Pitch
The fin pitch (distance between adjacent fins) typically spans 1mm–8mm. A tighter pitch (e.g., 1mm–3mm) packs more fins per unit
length, enhancing surface area for high - density heat transfer. Wider pitches (4mm–8mm) reduce airflow resistance, ideal for low
- pressure or high - viscosity fluid systems.
Fin Height
Fin height (from the tube surface to the fin tip) ranges from 5mm–30mm. Taller fins (20mm–30mm) amplify heat - dissipation area,
suiting high - temperature applications (e.g., boiler economizers). Shorter fins (5mm–15mm) balance efficiency and compactness for
space - constrained designs (e.g., automotive radiators).
We offer a flexible range of base tube diameters, from 12mm (small - scale precision applications) to 100mm+ (large - flow
industrial systems). Common sizes like 19mm, 25mm, and 38mm suit most standard heat - exchange setups, while custom diameters
address specialized flow and pressure needs.
Fin Pitch
The fin pitch (distance between adjacent fins) typically spans 1mm–8mm. A tighter pitch (e.g., 1mm–3mm) packs more fins per unit
length, enhancing surface area for high - density heat transfer. Wider pitches (4mm–8mm) reduce airflow resistance, ideal for low
- pressure or high - viscosity fluid systems.
Fin Height
Fin height (from the tube surface to the fin tip) ranges from 5mm–30mm. Taller fins (20mm–30mm) amplify heat - dissipation area,
suiting high - temperature applications (e.g., boiler economizers). Shorter fins (5mm–15mm) balance efficiency and compactness for
space - constrained designs (e.g., automotive radiators).
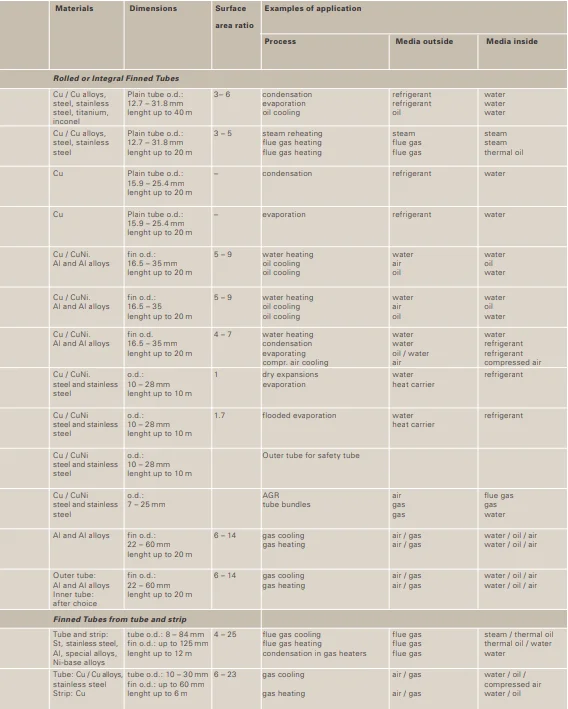
Material Options
Base Tube Materials
* Carbon Steel (e.g., Q235, ASTM A106): Cost - effective, with good thermal conductivity. Best for non - corrosive, moderate -
temperature environments (e.g., general industrial heating).
* Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316L): Superior corrosion resistance for aggressive media (acids, salts) or high - hygiene settings
(food processing, pharmaceuticals). Retains strength at elevated temperatures.
* Copper/Copper Alloys (e.g., C12200): Exceptional thermal conductivity (ideal for refrigeration, HVAC condensers). Suits low -
to - medium temperature, non - corrosive applications.
* Aluminum/Aluminum Alloys: Lightweight, corrosion - resistant, and cost - effective. Common in automotive cooling systems, air -
conditioning units.
Fin Materials
* Aluminum (1050, 6063): Dominant choice—lightweight, high thermal conductivity, and easy to form. Resists oxidation, ideal for
air - cooled systems (HVAC, radiators).
* Copper: Matches copper base tubes for maximum heat transfer (critical in refrigeration, cryogenics). Higher cost but unrivaled
performance in low - temperature applications.
* Stainless Steel: Paired with stainless - steel base tubes for extreme corrosion resistance (chemical plants, marine systems).
Compromises slightly on thermal conductivity for durability.
* Carbon Steel (e.g., Q235, ASTM A106): Cost - effective, with good thermal conductivity. Best for non - corrosive, moderate -
temperature environments (e.g., general industrial heating).
* Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316L): Superior corrosion resistance for aggressive media (acids, salts) or high - hygiene settings
(food processing, pharmaceuticals). Retains strength at elevated temperatures.
* Copper/Copper Alloys (e.g., C12200): Exceptional thermal conductivity (ideal for refrigeration, HVAC condensers). Suits low -
to - medium temperature, non - corrosive applications.
* Aluminum/Aluminum Alloys: Lightweight, corrosion - resistant, and cost - effective. Common in automotive cooling systems, air -
conditioning units.
Fin Materials
* Aluminum (1050, 6063): Dominant choice—lightweight, high thermal conductivity, and easy to form. Resists oxidation, ideal for
air - cooled systems (HVAC, radiators).
* Copper: Matches copper base tubes for maximum heat transfer (critical in refrigeration, cryogenics). Higher cost but unrivaled
performance in low - temperature applications.
* Stainless Steel: Paired with stainless - steel base tubes for extreme corrosion resistance (chemical plants, marine systems).
Compromises slightly on thermal conductivity for durability.
Video presentation
Manufacturing Technique
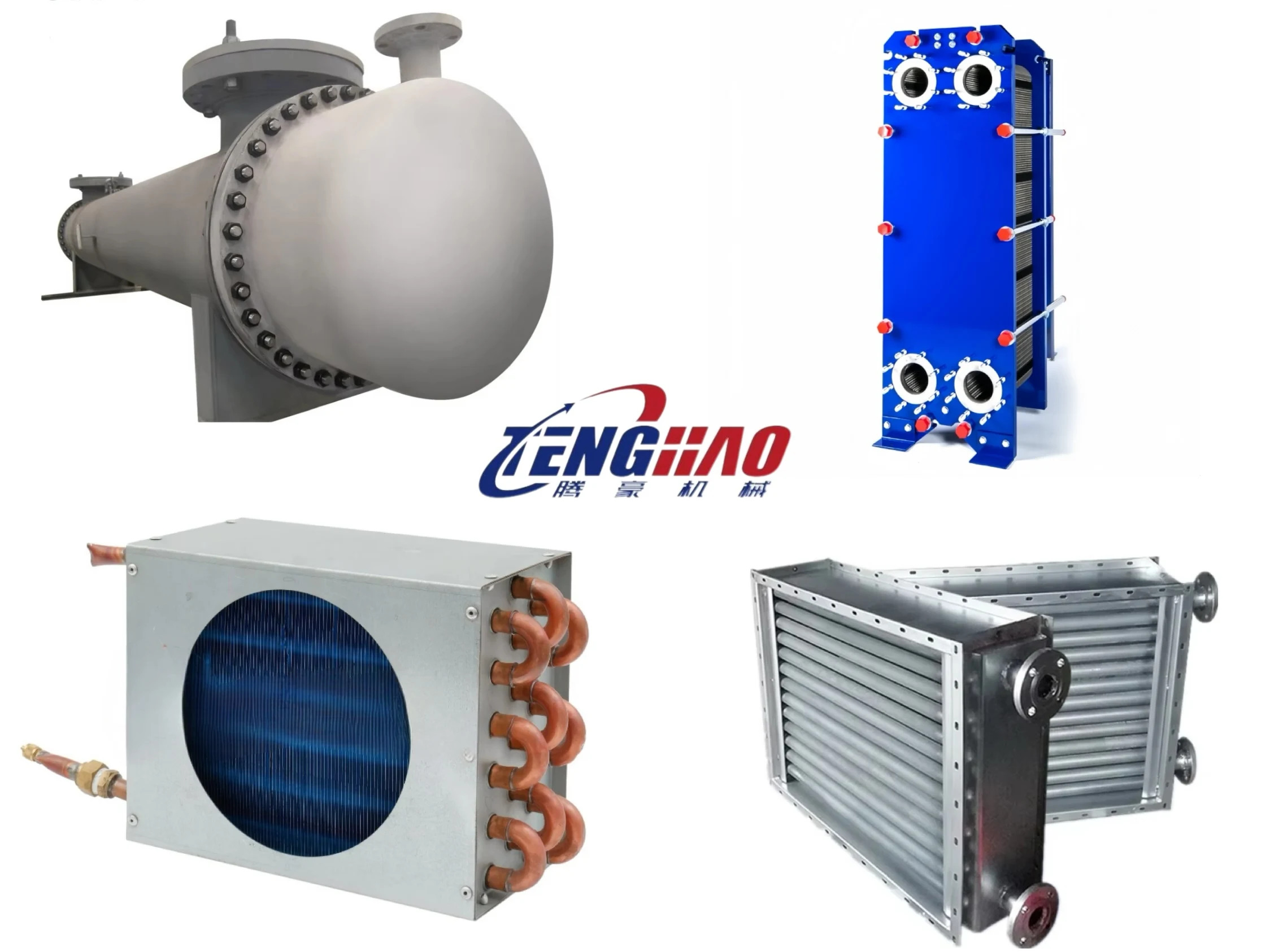
Application Scenarios
* HVAC & Refrigeration: Central air - conditioning units, chillers, and freezer condensers rely on spiral fin tubes to
cool/refrigerate air efficiently.
* Industrial Heat Exchangers: Power plants (boiler economizers, condenser tubes), chemical processing (reboilers, condensers),
and oil/gas refining (heat recovery units) use these tubes to manage high - temperature/pressure cycles.
* Automotive & Transportation: Radiators, intercoolers, and engine oil coolers leverage spiral fins for compact, high -
efficiency cooling in vehicles.
* Renewable Energy: Solar thermal collectors and geothermal heat pumps use spiral fin tubes to transfer heat between renewable
energy sources and working fluids.
cool/refrigerate air efficiently.
* Industrial Heat Exchangers: Power plants (boiler economizers, condenser tubes), chemical processing (reboilers, condensers),
and oil/gas refining (heat recovery units) use these tubes to manage high - temperature/pressure cycles.
* Automotive & Transportation: Radiators, intercoolers, and engine oil coolers leverage spiral fins for compact, high -
efficiency cooling in vehicles.
* Renewable Energy: Solar thermal collectors and geothermal heat pumps use spiral fin tubes to transfer heat between renewable
energy sources and working fluids.



Recommend Products

Company Profile


Product packaging

Contact information

FAQ
Q:Worry about your money? A: Trade Assurance can protect your money. (more information, pls contact me) Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ? A: We are factory.specilizing in heat exchanger for over 10 years. Q:Are your products customized? A:Yes,the products in the website are only the common type or the previous types from other customers,we can supply the newproducts according to your requirements or drawings. Q: How long is your delivery time? A: Generally it is 10-15 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity. Q: WHY CHOOSE US? A:We have strong technical force, with more than 10 years of experience in research and development of heat exchangers,We are committed to providing our customers with the most suitable heat transfer equipment and efficient energy saving needs.


