An Industrial Heat Exchanger is a cornerstone of modern thermal management, playing an indispensable role in processes across countless sectors. These devices are engineered to transfer thermal energy between two or more fluids, enabling precise temperature control, energy recovery, and enhanced operational safety. For any facility looking to optimize its processes, understanding how to select, operate, and maintain the right heat exchanger is paramount to achieving efficiency and sustainability goals. This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of this critical technology.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Heat Exchanger Design
The effectiveness of any heat exchange process hinges on its core fundamentals, primarily Heat Transfer Technology and thoughtful Heat Exchanger Design. The primary goal is to maximize the rate of heat transfer in a compact, cost-effective, and durable package. This is often achieved through innovative designs that increase the surface area available for transfer, such as the use of state-of-the-art tube arrangements. For example, a unit built with premium stainless steel and optimized heat-exchange tubes ensures maximum efficiency in thermal energy transfer. This precision engineering not only facilitates lightning-fast heat exchange but also guarantees the reliability needed for demanding industrial environments.
A Guide to the Common Types of Heat Exchangers
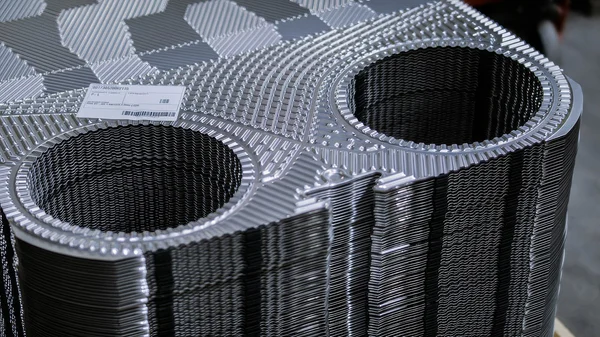
There are several Types of Heat Exchangers, each suited for different pressures, temperatures, and fluid properties. The most common varieties include shell-and-tube, air-cooled, and plate-and-frame exchangers. Plate Heat Exchangers, for instance, are known for their high efficiency and compact footprint, utilizing a series of stacked plates to create complex flow channels. Shell-and-tube designs are robust and versatile, making them a staple in oil refineries and chemical plants. The selection process involves a careful analysis of the operational requirements to match them with the most suitable Heat Exchanger Design, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Key Heat Exchanger Applications Across Industries
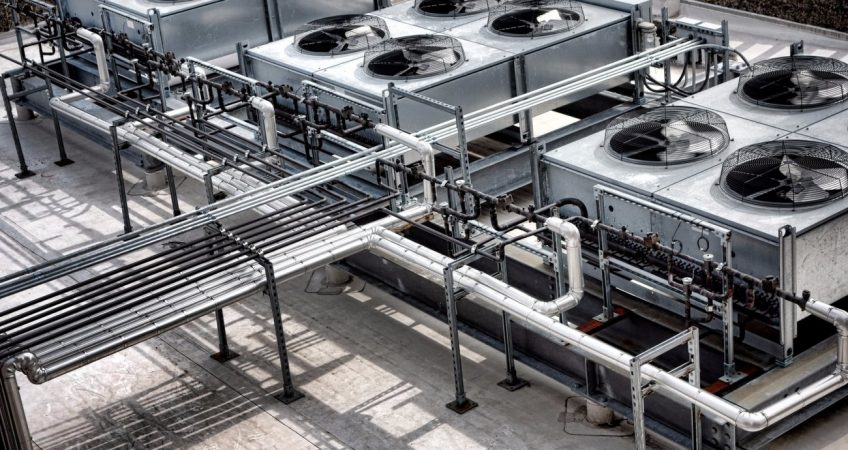
Versatility is a defining feature of the modern Industrial Heat Exchanger. The range of Heat Exchanger Applications is vast, extending from manufacturing plants that require precise temperature regulation to energy-intensive industries focused on improving thermal utilization. In food and beverage production, they are used for pasteurization and sterilization. In the chemical and petrochemical sectors, they are vital for controlling reaction temperatures and condensing vapors. A key driver across all these applications is Heat Exchanger Efficiency. By effectively recovering and reusing waste heat, these systems significantly lower energy costs, reduce an organization's carbon footprint, and contribute to more sustainable industrial operations.
A Practical Guide to Heat Exchanger Maintenance
To ensure consistent performance and a long operational lifespan, a structured approach to Heat Exchanger Maintenance is essential. Over time, issues like fouling, scaling, and corrosion can drastically reduce efficiency and even lead to system failure. Regular inspection and cleaning are crucial steps in any maintenance plan. However, the initial choice of equipment can significantly impact long-term maintenance needs. A modern Industrial Heat Exchanger constructed from durable stainless steel naturally resists corrosion and wear, minimizing downtime and repair costs. While a robust build reduces the frequency of interventions, a proactive maintenance schedule remains the best practice for ensuring peak Heat Exchanger Efficiency and protecting your investment.





![[Wuxi Tenghao Machinery ] - Leading Manufacturer of Industrial Heat Exchangers](https://ptwebimg.pinshop.com/i/2025/05/29/e7pb3m-3.jpg)