Product Design Content
1. Overall Structure Design
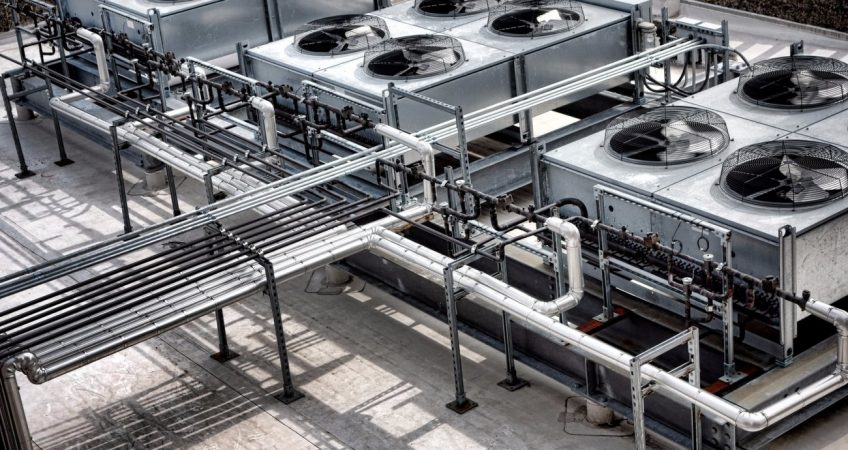
The heat exchanger adopts a fin - tube structure. The main body consists of a large number of closely arranged fins (the red - brown parts in the picture) and copper tubes (the metallic tubes connecting the fins). The fins increase the heat transfer area, and the copper tubes are used to transport the heat - carrying fluid. The frame structure (the metal frame surrounding the fins and tubes) provides structural support and protection, ensuring the integrity of the heat exchanger during transportation, installation, and use.
2. Material Selection Design
- Fins: Likely made of aluminum alloy. Aluminum has good thermal conductivity, is lightweight, and has relatively low cost, which is very suitable for use as fins to enhance heat transfer. The surface may be treated (such as oxidation) to improve corrosion resistance.
- Copper Tubes: Copper is chosen for its excellent thermal conductivity, which can effectively transfer heat. Copper also has good corrosion resistance in many fluid media, ensuring a long service life of the tubes.
- Frame: Probably made of stainless steel. Stainless steel has high strength, good corrosion resistance, and can protect the internal heat exchange components from external mechanical damage and environmental corrosion.
3. Heat Transfer Design
The design of the fin - tube structure is to maximize heat transfer efficiency. The fins are closely attached to the copper tubes, so that the heat in the fluid inside the tubes can be quickly transferred to the fins, and then dissipated into the surrounding air (or other heat - exchanging media). The spacing and shape of the fins are carefully designed. An appropriate fin spacing can ensure sufficient air flow, avoid excessive air resistance, and also ensure that the fins can effectively exchange heat with the air. The shape of the fins (such as the corrugated shape in the picture) can also increase the turbulence of the air flow, thereby enhancing the heat transfer effect.
4. Installation and Connection Design
The heat exchanger is designed with inlet and outlet pipes (the metallic pipes extending from the side). These pipes are used to connect to the external fluid circulation system, allowing the heat - carrying fluid (such as refrigerant, cooling water) to enter and exit the copper tubes of the heat exchanger. The installation of the heat exchanger can be fixed through the frame, and it can be installed in various industrial equipment or air - conditioning and refrigeration systems according to actual needs, such as being installed in a cabinet or on a support frame.





![[Wuxi Tenghao Machinery ] - Leading Manufacturer of Industrial Heat Exchangers](https://ptwebimg.pinshop.com/i/2025/05/29/e7pb3m-3.jpg)