Introduction to Fin - Tube Heat Exchangers
Fin - tube heat exchangers are indispensable in modern industrial thermal management. Their design, combining rows of fins and copper tubes, creates a large surface area for efficient heat transfer. Whether in HVAC systems regulating building temperatures or industrial cooling processes safeguarding machinery, they play a critical role.
Design and Structure
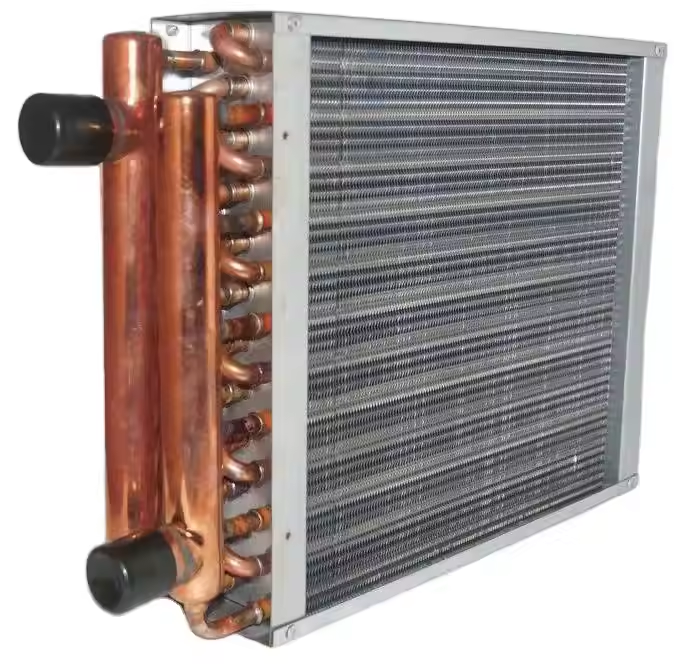
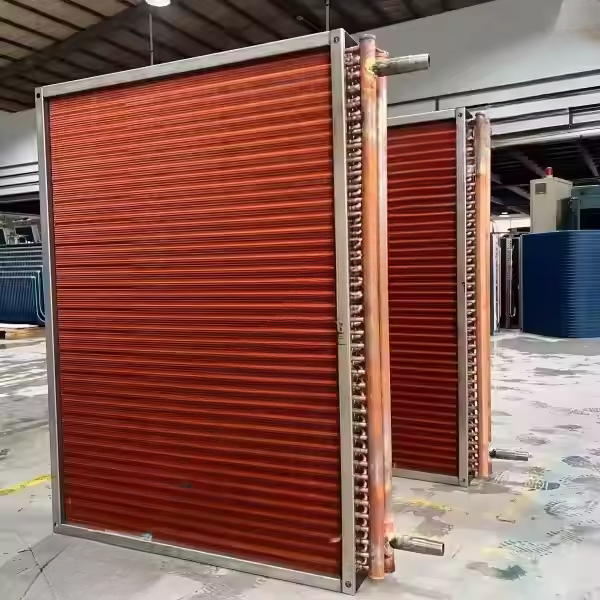
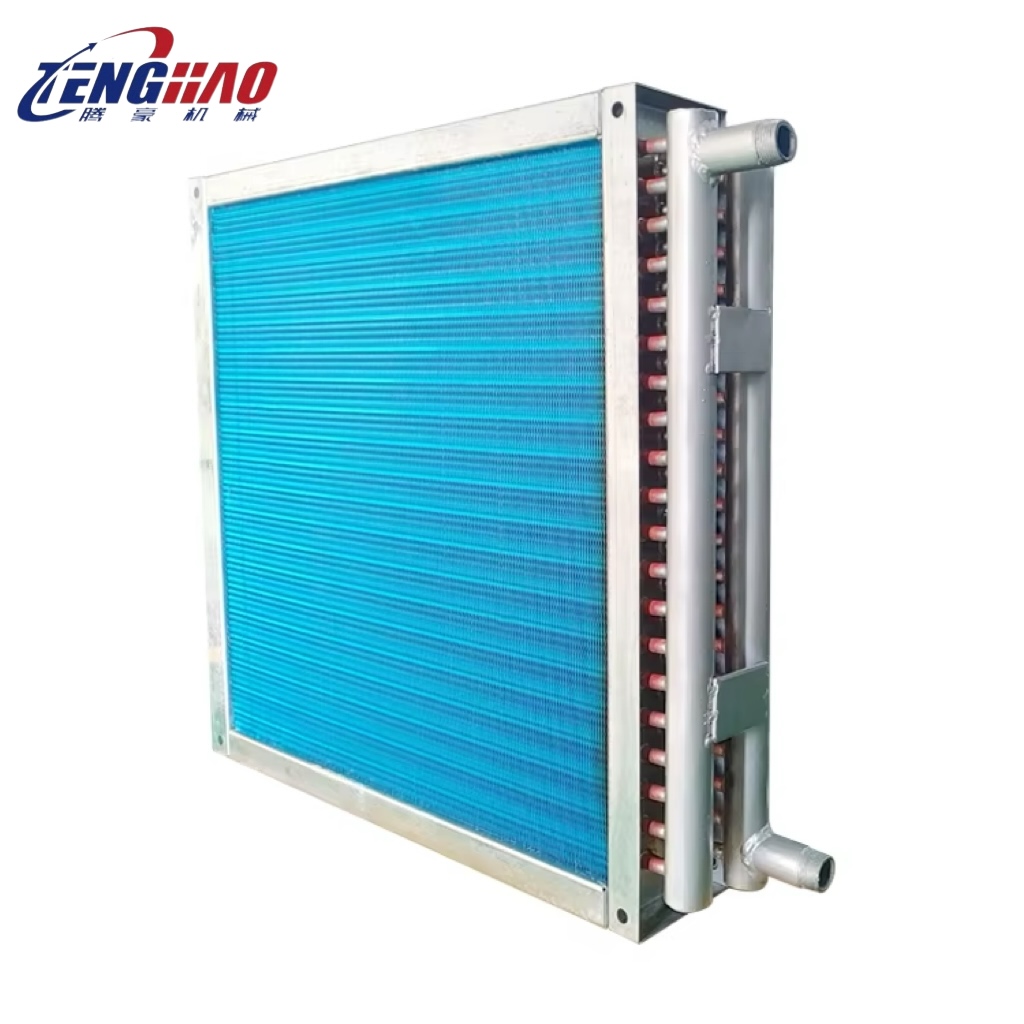
At the heart of these exchangers are the fins and copper tubes. The fins, typically made of aluminum for excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, are stacked closely. Copper tubes run through them, acting as channels for heat - carrying fluids (like refrigerants or cooling water). This structure ensures that heat from the fluid inside the tubes is quickly transferred to the fins and then dissipated into the surrounding air or other media. The metal frame surrounding the assembly provides structural stability, protecting the delicate fins and tubes during transportation, installation, and operation.
Applications Across Industries
- HVAC Systems: In heating and cooling systems, fin - tube heat exchangers help regulate air temperature. They absorb heat from warm air (for cooling) or release heat to cold air (for heating), ensuring comfortable indoor environments in commercial buildings, offices, and residential complexes.
- Refrigeration: In refrigeration units, like cold storage facilities and commercial freezers, these exchangers remove heat from the internal space, maintaining low temperatures crucial for preserving food, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature - sensitive goods.
- Industrial Cooling: Manufacturing processes, such as metalworking or chemical production, generate excess heat. Fin - tube heat exchangers cool down machinery and process fluids, preventing overheating and ensuring stable, efficient operations.
Advantages of Fin - Tube Heat Exchangers
- High Heat Transfer Efficiency: The fin - tube design maximizes the contact area between the fluid and the surrounding air, enabling rapid heat exchange. This means systems using these exchangers can achieve desired temperature changes more quickly, saving energy.
- Compact and Space - Saving: Compared to some bulkier heat exchange solutions, their stacked structure allows for effective heat transfer in a relatively small footprint. This is a huge advantage in industrial settings or building mechanical rooms where space is limited.
- Durability: With materials like copper (for tubes) and treated aluminum (for fins), they resist corrosion and wear. Properly maintained, they can serve industrial applications for years, reducing replacement costs.
Choosing the Right Fin - Tube Heat Exchanger
When selecting a fin - tube heat exchanger, consider factors like:
- Application Requirements: Different industries and systems have unique heat transfer needs. For example, a refrigeration system for a pharmaceutical warehouse may need stricter temperature control than a general industrial cooling setup.
- Fluid Compatibility: Ensure the materials of the tubes and fins are compatible with the heat - carrying fluid. Some chemicals may corrode certain metals, so material selection is vital for long - term performance.
- Size and Capacity: Match the exchanger’s size and heat transfer capacity to the system’s demands. An undersized unit will struggle to maintain temperatures, while an oversized one may waste energy and space.